Chapter catalogue
- Entitlements provided by Labour legislation for part-time employees
- Other entitlements for employees employed on continuous contracts
- Q&A
- How to calculate ADW and related statutory entitlements of eligible short-time employees?
- The basis for calculating the items of statutory entitlements
- How can Workstem users easily deal with tedious payroll calculation?
Because of its flexibility to meet the needs of business operations, employers are most likely to take on part-time/temporary employees in their own catering, construction or retail businesses. “Especially during the pandemic, companies hire part-time employees at every turn.” Mr. Cheung said in an interview. On the other hand, when it comes to dealing with human resources, employers and HR generally agree that part-time jobs have fewer entitlements than permanent ones, even if some of them don’t say so. But is it true? Workstem has compiled a legal breakdown of part-time employees that everyone in Hong Kong is reading.
David often received emails from the new employer in the background. As the payday approached, Aaron, the employer of a large catering company, anxiously asked us how to calculate payroll when employees had paid holidays. He also wondered whether unpaid rest days should be deducted when calculating ADW.
He even paid part-time employees more money for the previous two months because of the same problem. “I can’t afford to lose if I don’t understand the rules,” he said.
Aaron’s case is no accident. Nowadays, more and more people are focusing on business development, but not paying enough attention to HR laws until they make a big mistake. To solve the problem of Aaron, we start from the understanding of the law!
Entitlements provided by Labour legislation for part-time employees
Employee basic entitlements
According to the labour law, part-time employees enjoy the same protection provided by the law as full-time employees. Regardless of the difference in the title of the position they were hired, and regardless of the employees’ working hours, they all enjoy the following rights.
Under Labour legislation, part-time employees enjoy the same protection as full-time employees. Regardless of the employees’ positions or working hours, they are entitled to the following entitlements.
- Salary payment protection
- Maternity protection (prohibiting employers from assigning pregnant employees to heavy, dangerous or harmful work)
- Salary deduction limits
- Employment protection (unreasonable and unlawful dismissal)
- Statutory holidays
- Employer’s obligation to provide employment information, etc.
Other entitlements for employees employed on continuous contracts
In addition, Ordinance 418 provides that an employee is entitled to a continuous contract of statutory holidays, rest days and paid holidays provided that he has been employed by the same employer for four weeks or more and has worked at least 18 hours per week. Of course, both permanent and temporary employees who meet the conditions of Ordinance 418 are also protected by the following Ordinance 418.
However, the Labour Department is reviewing the Ordinance 418 in 2023, and plans to change it to 4 weeks of total working hours as the basis. Employees are required to meet different working hour requirements within four weeks, namely 72, 68, 64 and 60 hours, to enjoy more statutory employment rights.
Employee, no mather permanent employees or a casual worker, as long as they meet the conditions of 418, are also entitled to the following:
- Rest days (6 working days and 1 rest day)
- Maternity leave and maternity leave pay
- Statutory holiday pay
- Paternity leave
- Paid annual leave
- Severance payment
- Sick leave allowance
- Long service payment, etc.
Note: Employees are eligible for the above entitlements after meeting the requirements of Ordinance 418. Please click the link for more restrictions on employee allowance payment. This article takes statutory holiday pay as an example. Employees who meet the continuous contract employment basis must have been employed for 3 months before they are entitled to holiday pay. Same with annual leave, maternity leave, etc.
Q&A
A simple example, Jayson worked at a steakhouse due to insufficient income, and worked 16, 18, 20, and 18 hours in the first week to the fourth week respectively.
According to Ordinance 418, since he has been employed continuously for 4 weeks and the total working hours have reached 72 hours, he is entitled to the above qualifications.
At the beginning of the next month, the Mid-Autumn Festival was a statutory holiday. The employer gave Jayson a holiday but did not pay him for it. Jayson objected that the employer should pay him according to the law.
David: Jayson is eligible under Ordinance 418, so he is employed on a continuous contract and is entitled to the above entitlements. However, Jayson is not officially eligible for holiday pay because he has not yet met the Employment Ordinance which requires an employee to remain employed for three months. Employers should stop foolishly paying extra allowances!
In short, part-time employees in a company are employed on a continuous contract when they meet a fixed number of working hours per week and are employed continuously for one month. However, if the above allowances are actually paid, it is necessary to double check whether the continuous contract employees meet the requirements according to the legal rules and regulations to avoid extra rations! On the other hand, which legislation should we refer to to ensure accurate payroll calculation to eligible part-time employees during payroll calculation and payment?
How to calculate ADW and related statutory entitlements of eligible short-time employees?
Introduction to Ordinance 713
Ordinance 713 provides that the statutory entitlements of an employee, regardless of his or her remuneration scheme, including monthly salary, piece-by-piece daily salary, etc., shall normally be calculated on the basis of the 12-month average daily wage and the “not included *” pay shall be excluded from the calculation of wages.
*Wages not counted:
To calculate ADW, identify the circumstances in which no or all wages are paid as specified in the Employment (Amendment) Ordinance 2007 and exclude the period together with the wages received by the employees therein:
(i) Employees take any of the following leaves: Rest days, statutory holidays, annual leave, maternity leave, paternity leave or sick leave industrial injury sick leave as specified in the Employees’ Compensation Ordinance or leave delegated by the employer.
(ii) Employees are not offered work by their employers on normal working days.
Aaron: “I can also check these laws. What is the specific plan of holiday pay for part-time jobs? ”
David: “Don’t worry, I’ll tell you in detail.”
In real life when it comes to the issue of human capital, we must not be as eager as long. Let’s take a look at how other allowances are calculated and paid apart from holiday pay.
The basis for calculating the items of statutory entitlements
Under the supplement to Ordinance 713, the employer is required to use the average daily (or monthly) wage earned by the employee in the 12 months preceding the specified date as the basis for the calculation of the statutory entitlements. If the employee has been employed for less than 12 months, the shorter period will be used.
The “specified dates” for each relevant statutory entitlement are as follows:
| Statutory Entitlements | Day(s) of Leave | Specified Dates |
| Holiday Pay | 1 day | Day of the statutory holiday |
| More than 1 consecutive day | First day of the statutory holidays | |
| Annual Leave Pay | 1 day | Day of the annual leave |
| More than 1 consecutive day | First day of the annual leave | |
| Day(s) of untaken leave upon termination of contract | Date of termination of contract | |
| Sickness Allowance | 1 day | The sickness day |
| More than 1 consecutive day | The first sickness day | |
| Maternity Leave Pay | More than 1 consecutive day | First day of the maternity leave |
| Paternity Leave Pay | 1 day | Day of the paternity leave |
| More than 1 consecutive day | First day of the paternity leave | |
| Payment in lieu of notice |
|
The day when a notice of termination of contract is given(Note11) |
| End of Year Payment(Note12) |
|
Due day of the payment |
Let’s take a look at some examples to get a better understanding of this concept.
Example 1: Aaron’s company has a part-time employee, Amy, who started her job on January 1st, 2007. How should we calculate her holiday salary on January 1st, 2008?
David: According to Aaron’s description, Amy started to work in 2007. After referring to the above table, we find that the specified date of holiday pay is statutory holiday, and we calculate the 12-month average daily salary based on the total income Amy earned from January 1st to December 31st, 2007.
Assuming that Amy’s daily salary is HK$300, the total number of days he worked in 2007 is 301 (that is, 365 days -52 rest days -12 statutory holidays). In addition, her 8-day holiday salary is HK$2,800. So its total income is:
2,800+301*300=HK$92,700
Periods and amounts not counted by Amy are: 52 days unpaid rest days and 4 days unpaid statutory holidays (no statutory holiday pay for the first 3 months)
To sum up, amy’s adw calculation formula is :(92,700-0)/(365-52-4)=HK$300
Example 2: Eva is a part-time employee who gave Aaron a headache recently. She started her job on August 1st and has been a continuous contract employee for more than 3 months. In this case, should Aaron pay her holiday salary next month on September 22nd, the day after the Mid-Autumn Festival?
Even though Eva is a part-time employee employed on a continuous contract and is entitled to statutory holidays, she has not been employed for more than three months because she has not met the Employment Ordinance rules relating to leave pay. So Aaron doesn’t have to pay for her holiday pay.
How can Workstem users easily deal with tedious payroll calculation?
Aaron often complained that dealing with HR problems distracted him. As mentioned in this article, the problems caused by unprofessionalism even caused the excessive compensation, which would make his pocket empty.
After using the one-stop HR management system Workstem, you only need to import employee information or create a new employee profile with one click, and the system can autopay on time and accurately every month according to the rules. Not only part-time/short-time employees’ salary and allowance, but also more complex HR tasks we can handle!
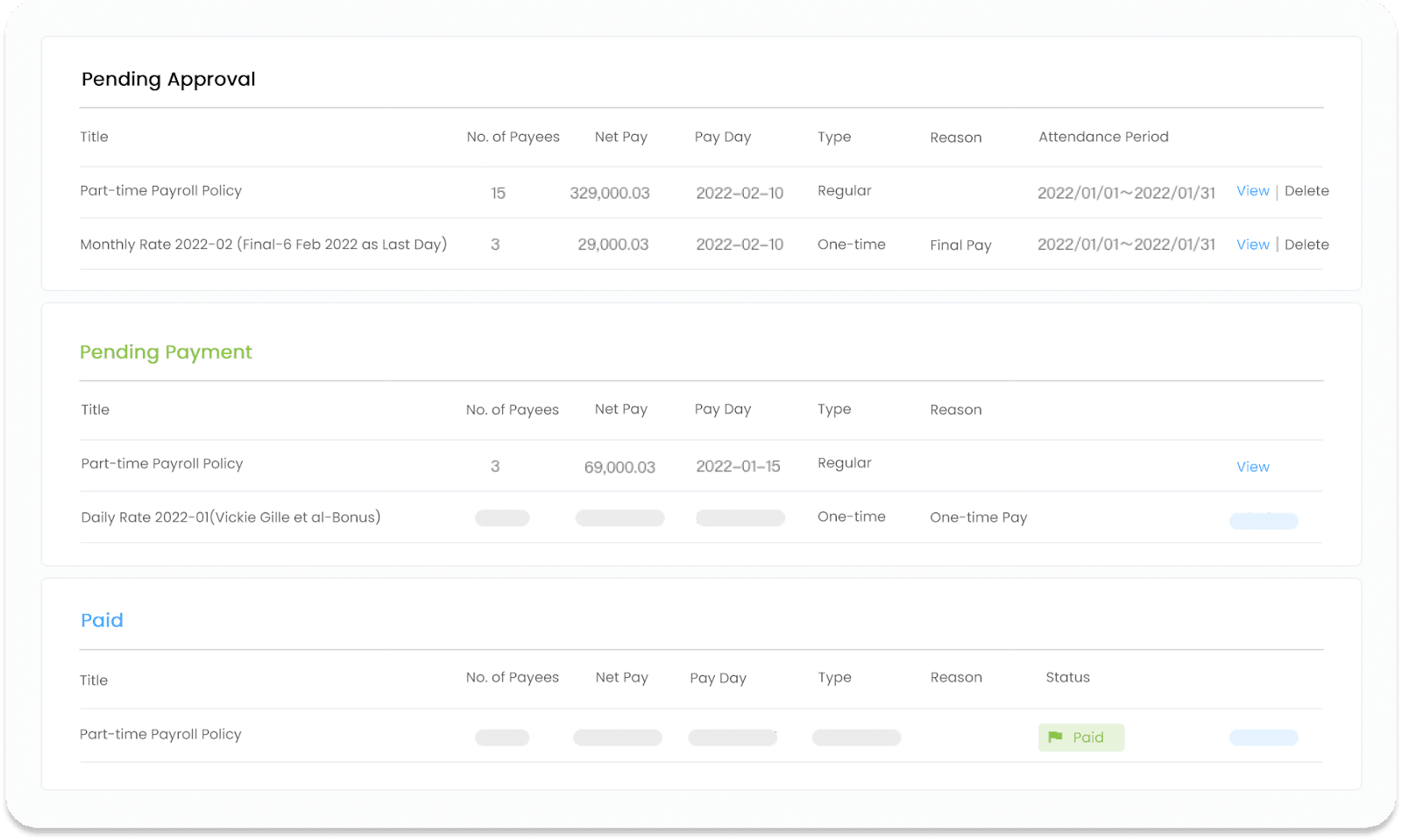
David: “In fact, employers who are troubled by the company’s business development should use an intelligent human resource software that can save worry and effort to solve the human resources problem. For your information, click the link below to use your 14-day Workstem account for free and unlock new ideas for more HR issues!”
Read More: Many Part-time Employees? How to Take Care of the “418” Rule?
(The content and information in this article are for reference only. The accuracy and reliability of the information are subject to the latest government regulations. If you want to reprint the article or content, please contact us first or attach a link to this article, and indicate the source of reprint.)







![[418 Guide] Ordinance 418 And Continuous Contract](https://www.workstem.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Untitled-design-min-350x220.png)